Contributed by: Rouhea
Thanks to:
Nigel_Samhain
Submitted: 03-04-2003
The
difference between fog and mist is the particle size
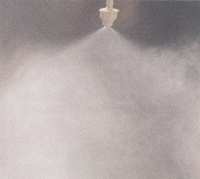
generated.  Fog Fog
Any water droplet smaller
than 50 microns is considered fog. There is 'wet' fog
and 'dry' fog. Wet fog has a particle size in the range
of 10-50 microns. Dry fog is produced by ultrasonic
systems and has particles in the range of 2-10 microns.
Dry fogging systems use very little water, but
they do require a high quality supply (ie. R.O. or
distilled), as they are prone to clogging.
 The disadvantage of dry fogging systems
is that they are no good for cooling, since the quantity
of water available for evaporation is small. Wet fogging
systems can be run to excess during summer and the
surplus fog can be vented. The disadvantage of dry fogging systems
is that they are no good for cooling, since the quantity
of water available for evaporation is small. Wet fogging
systems can be run to excess during summer and the
surplus fog can be vented.
Fogging systems
require additional watering of the cuttings, unlike
conventional misting systems.
 Misting systems are the cheapest to set
up and run, but fogging systems may give better results
with some plant species, for example some Verticordias,
Brachycome, lavenders, and many species with hairy or
finely divided leaves. Misting systems are the cheapest to set
up and run, but fogging systems may give better results
with some plant species, for example some Verticordias,
Brachycome, lavenders, and many species with hairy or
finely divided leaves.
Misting
Misting maintains a fully
saturated atmosphere around the cuttings, whereas
fogging aims to keep the leaves cool. Reducing leaf
temperature reduces the water vapor pressure within the
leaf and less water escapes. However, a fully saturated
atmosphere will not entirely prevent transpiration water
loss from cuttings. If the leaf temperature exceeds the
air temperature, then the internal vapor pressure will
be greater than the surrounding air, and there will be
evaporation from the leaf. To avoid this, shading is
necessary to prevent high leaf temperatures.
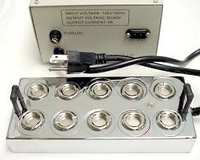
(Nigel_Samhain) The foggers usually use a
diffuser, although they call it a ceramic disc coated
with what appears to be brass. These foggers produce
vapors in the 2-15 micron range. When applied to the
root system, it is comparable to growing your plants
within a cloud.
Foggers experience calcification.
Usually it can be cleaned off with a dilute
solution of White vinegar. When the EC of the solution
is high, the calcification occurs at a much greater
rate.
It is recommended that the fog be
dispersed in increments, rather than remain constant, to
cut back on diffuser wear. This also tends to make the
roots strive for faster growth.
|