What are trichomes? Trichome 101
| Added by:
10k Last edited by:
10k Viewed: 734 times |
Rated by 240 users:
9.66/10 |
Contributed by: Snaps_provolone
Submitted June 18, 2003 What
are Trichomes?

capitate stalked trichome photo
by: Eirik
Although cannabis
resin glands called trichomes are structurally diverse,
they come in three basic varieties:
Bulbous:
The bulbous type is the
smallest (15-30 micron). From one to four cells make up
the "foot" and "stalk," and one to four cells make up
the "head" of the gland. Head cells secrete a resin -
presumably cannabinoids, and related compounds which
accumulate between the head cells and the cuticle. When
the gland matures, a nipple-like protrusion may form on
the membrane from the pressure of the accumulating
resin. The bulbous glands are found scattered about the
surfaces of the above-ground plant parts.
Capitate-Sessile:
The second type of
gland is much larger & is more numerous than the
bulbous glands. They are called capitate, which means
having a globular-shaped head. On immature plants, the
heads lie flush, appearing not to have a stalk and are
called capitate sessile. They actually have a
stalk that is one cell high, although it may not be
visible beneath the globular head. The head is composed
of usually eight, but up to 16 cells, that form a convex
rosette. These cells secrete cannabinoids, and related
compounds which accumulate between the rosette and it's
outer membrane. This gives it a spherical shape. The
gland measures from 25 to 100 micron across.
Capitate-Stalked:
Cannabinoids are most
abundant in the capitate-stalked gland which
consists of a tier of secretory disc cells subtending a
large non-cellular secretory cavity. During flowering
the capitate glands that appear on the newly formed
plant parts take on a third form. Some of the glands are
raised to a height of 150 to 500 micron when their
stalks elongate. These capitate-stalked glands appear
during flowering and form their densest cover on the
female flower bracts. They are also highly concentrated
on the small leaves that accompany the flowers. The male
flowers have stalked glands on the sepals, but they are
smaller and less concentrated than on the female bracts.
Male flowers form a row of very large capitate glands
along the opposite sides of anthers.
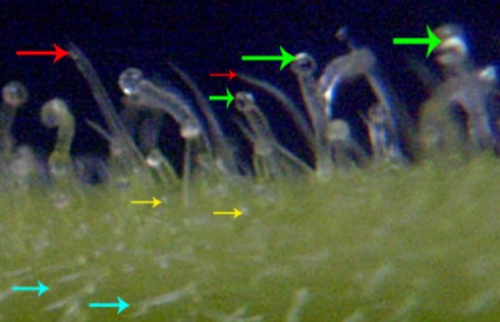
photo by:
Proof_of_the_pudding

photo by:
Proof_of_the_pudding
The figures above denote
capitate-stalked trichomes with green arrows, the
bulbous trichomes with yellow arrows & the red
arrows mark the capitate-sessile trichomes. Cyan arrows
denote cystolith hairs.
Life inside a capitate-stalked
trichome
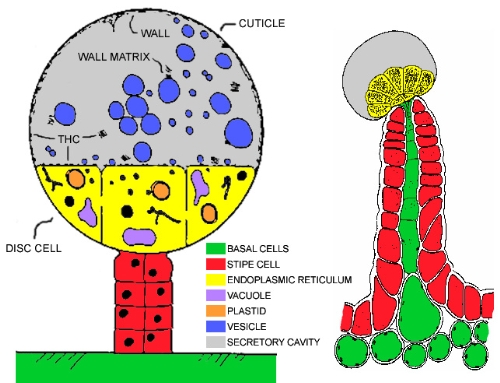
image by:
Snaps_Provolone
Disc cells, attached
to leaf or bract by stipe cells (RED) & basal cells
(GREEN), release
fibrillar wall matrix into secretory cavity where it
contributes to thickening of subcuticular wall during
enlargement of secretory cavity. Plastids (ORANGE) in disc cells
produce secretions called lipoplasts which synthesize
quantities of lipophilic substances that accumulate
outside the plasma membrane, migrating into the
endoplasmic reticular cytoplasm and through the plasma
membrane and cell wall into the secretory cavity where
they form vesicles (BLUE) in the secretory
cavity. Vesicles in contact with the subcuticular wall
release contents that contribute to the growth of the
cuticle during the enlargement of the secretory cavity.
THC occurs in the walls, fibrillar matrix & other
contents surrounding the vesicles, but not in the
vesicles. Trace amounts of THC is present in the disc
cells.
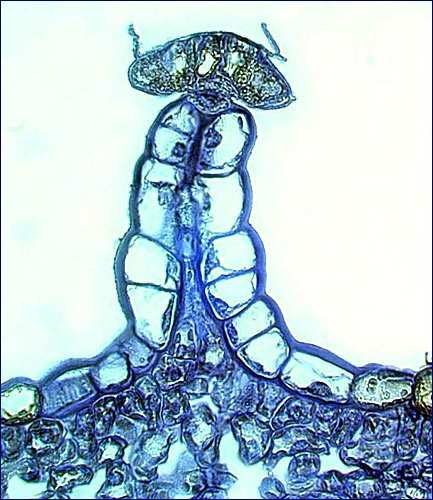
photo by:
Eirik
When to
harvest your trichomes
There are several
schools of thought as to when it is the time to harvest.
I shall attempt to explain how you can determine the
harvesting time that will produce the most favorable
psychoactive effect for your individual preferences.
We are most concerned with the capitate-stalked
trichomes, as these contain the overwhelming majority of
the psychoactive cannabinoids (THC, THCV, CBN).
Different cannabinoids affect the high in a multifaceted
manner.
THC:
delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol &
delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol - THC mimics the action of
anandamide, a neurotransmitter produced naturally in the
body, which binds with the cannabinoid receptors in the
brain to produce the ?high? associated with marijuana.
THC possesses high UV-B (280-315 nm) absorption
properties.
THCV:
tetrahydrocannabivarin - prevalent
in certain South African and Southeast Asian strains of
cannabis. It is said to produce a ?clearer high? &
seems to possess many of the therapeutic properties of
THC.
CBD:
cannabidiol - previously believed to
be psychoactive, or to contribute to the high by
interacting with other cannabinoids, conversely the most
recent research indicates that CBD has negligible effect
on the high, it is however a strong anti-inflammatory,
and may take the edge off some THC effects, such as
anxiety. CBD as a non-psychoactive cannabinoid appears
to be helpful for many medical conditions. CBD
biosynthesizes into cannabinol (CBN) &
tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
CBN:
cannabinol - a degradation product
of THC, produces a depressant effect, ?fuzzy? forehead.
CBC:
cannabichromene - non-psychoactive ,
a precursor to THC.
CBG:
cannabigerol - non-psychoactive,
hemp strains often posses elevated levels of CBG while
possessing only trace amounts of THC.
Heavy
trichome production is not necessarily an indication of
a potent plant. Some hemp strains have moderate layers
of trichomes yet pack only a strong headache. In a drug
strain, a thick layer of trichomes is a symbol that it
may well posses an elevated potency level, but it is
certainly not a guarantee.
What defines a
cannabis drug strain is the plant's ability to produce
THC & THCV.
A small 25x or stronger pocket
microscope, which can be picked up inexpensively at an
electronics store like Radio Shack, works well for
getting a closer peek at your trichome development. We
are examining are the capitate stalked glandular
trichomes, the coloration of these gland heads can vary
between strains and maturity. Most strains start with
clear or slightly amber heads which gradually become
cloudy or opaque when THC levels have peaked and are
beginning to degrade. Regardless of the initial color of
the secretory cavity, with careful observation you
should be able to see a change in coloration as
maturity levels off.
Some cultivators wait for
about half of the secretory cavities to go opaque before
harvesting, to ensure maximum THC levels in the finished
product. Of course nothing tells the truth more than
your own perception, so try samples at various stages to
see what is best for you & the phenotype your
are growing. While you may be increasing the total THC
level in the bud by allowing half of the glands to go
opaque, the bud will also have a larger percentage of
THC breakdown products such as CBN, which is why some
people choose to harvest earlier while most of the
secretory cavities are still clear.
Indica
varieties will usually have a 10-15 day harvest window
to work with. Sativas and Indica/Sativa hybrids often
have an extended period to work with.

photo by:
Eirik

photo by:
Proof_of_the_pudding
The figures above denotes clear
trichomes with green arrows, the cloudy trichomes with
yellow arrows & the red arrows mark the amber
trichomes.
Why did
trichomes evolve in nature?
Cannabis has
evolved trichomes for a multitude of uses in nature,
some of these require THC & other cannabinoids to be
effective, and others that do not.
Insect Protection:
Many insects find the
thick coating of trichomes unpleasant, this offers a
level of protection for the developing seeds.
Animals:
The layer of trichomes and
cystolith hairs makes cannabis less palatable to many
herbivores & omnivores.
Desiccation:
The layer of trichomes helps
to 'insulate' the pistilate (female) flower from low
humidity levels and high wind.
UV-B Light:
UV-B light is harmful to
living things, THC has very high UV-B adsorption
properties, thus cannabis evolution may have favored the
evolution of genotypes that produced these THC laden
capitate-stalked trichomes as a built in 'sun-screen'
for protection against UV-B light rays.
Fungal Protection:
Some of the compounds
present in the trichomes actually inhibit the growths of
some types of fungus.
Quite possibly, the most important reason for the
evolution of the THC laden capitate-stalked trichomes is
the intercession of man in the natural selection
process, favoring genotypes that produce copious amounts
of THC laden trichomes.
|
| Last modified: 18:56 - Jul 02,
2003 |
| |